
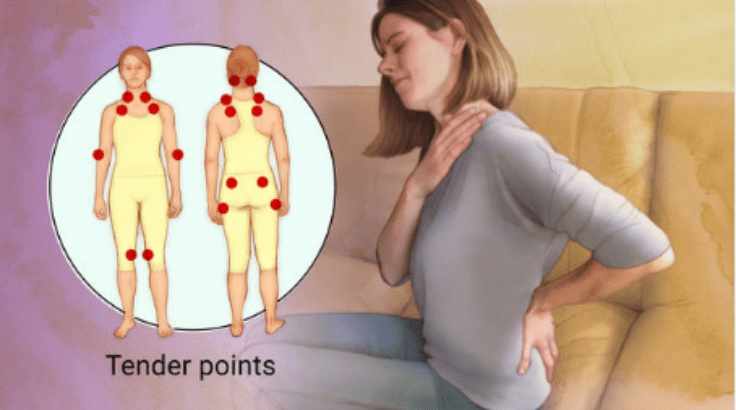
A meta-analysis compared objective and subjective sleep metrics in people with fibromyalgia and healthy people. These include a difficulty to fall asleep or stay asleep, awakening while sleeping and waking up feeling unrefreshed. Sleep problems are a core symptom in fibromyalgia. Physical fatigue can be demonstrated by a feeling of exhaustion after exercise or by a limitation in daily activities. Patients may experience physical or mental fatigue. Fatigue įatigue is one of the defining symptoms of fibromyalgia. According to the NHS, widespread pain is one major symptom, which could feel like: an ache, a burning sensation, or a sharp, stabbing pain. Pain įibromyalgia is predominantly a chronic pain disorder. Other symptoms may include heightened pain in response to tactile pressure ( allodynia), cognitive problems, musculoskeletal stiffness, environmental sensitivity, hypervigilance, sexual dysfunction, and visual symptoms.

The defining symptoms of fibromyalgia are chronic widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbance.
FIBRO TAKE AS NEEDED CODE
The International Classification of Diseases ( ICD-11) includes fibromyalgia in the category of "Chronic widespread pain", code MG30.01. įibromyalgia is classed as a disorder of pain processing due to abnormalities in how pain signals are processed in the central nervous system. The term "fibromyalgia" is from New Latin fibro-, meaning "fibrous tissues", Greek μυο- myo-, "muscle", and Greek άλγος algos, "pain" thus, the term literally means " muscle and fibrous connective tissue pain". Fibromyalgia was first defined in 1990, with updated criteria in 2011, 2016, and 2019. Rates appear similar in different areas of the world and among different cultures. Women are affected about twice as often as men. įibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2–4% of the population. While fibromyalgia is persistent in nearly all patients, it does not result in death or tissue damage. Q10 coenzyme and vitamin D supplements may reduce pain and improve quality of life. Other common helpful medications include serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRI), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and muscle relaxants. The medications duloxetine, milnacipran, or pregabalin have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the management of fibromyalgia.

The use of medication in the treatment of fibromyalgia is debated, although antidepressants can improve quality of life. Weak recommendations are given to mindfulness, psychotherapy, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, and meditative exercise such as qigong, yoga, and tai chi. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology strongly recommends aerobic and strengthening exercise. The treatment of fibromyalgia is symptomatic and multidisciplinary. The pain appears to result from processes in the central nervous system and the condition is referred to as a "central sensitization syndrome". Environmental factors may include psychological stress, trauma, and certain infections. The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Other symptoms include insomnia and a general hypersensitivity. Widespread pain, feeling tired, sleep problems īased on symptoms after ruling out other potential causes Īnemia, autoimmune disorders (such as ankylosing spondylitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, or multiple sclerosis), Lyme disease, osteoarthritis, thyroid disease ĭuloxetine, milnacipran, pregabalin, gabapentin įibromyalgia ( FM) is a medical condition defined by the presence of chronic widespread pain, fatigue, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and depression.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
